Introduction
The internet has transformed the world in unimaginable ways, evolving from a military communication network to an indispensable part of daily life. Understanding its history offers insight into how this revolutionary technology came to be, and what the future might hold. This article delves deep into the development, milestones, and key figures in the history of the internet.
The Birth of the Internet

Early Concepts and Theories
The seeds of the internet were sown in the minds of visionaries like J.C.R. Licklider, who imagined a globally interconnected set of computers through which everyone could quickly access data and programs from any site. This concept, known as the “Intergalactic Computer Network,” laid the foundation for future developments.
ARPANET: The First Network
The Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET), developed by the U.S. Department of Defense, was the first operational packet-switching network and the precursor to the internet. Launched in 1969, it connected four universities and marked the beginning of networked communication.
Packet Switching Technology
Packet switching, a method of data transmission in which data is broken into smaller packets before being sent, was crucial for the development of the internet. This technology, developed by Paul Baran and Donald Davies, allowed for more efficient and reliable communication.
The Expansion and Evolution
The Introduction of TCP/IP
In the late 1970s and early 1980s, Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn developed the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), which standardized data transmission across networks. TCP/IP became the backbone of the internet, allowing diverse networks to interconnect seamlessly.
The Birth of Email
Email, one of the first applications of the internet, was invented by Ray Tomlinson in 1971. His use of the “@” symbol to separate the user name from the computer name became a standard in email addresses.
The Development of Domain Names
As the number of internet users grew, the need for a more human-friendly addressing system became apparent. The Domain Name System (DNS) was introduced in 1983 by Paul Mockapetris, allowing users to access websites using easy-to-remember domain names instead of numerical IP addresses.
The World Wide Web
Tim Berners-Lee and the World Wide Web
In 1989, Tim Berners-Lee, a British scientist at CERN, proposed the World Wide Web, a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessible via the internet. By 1991, the first website was live, and the web began to grow rapidly.
The First Web Browsers
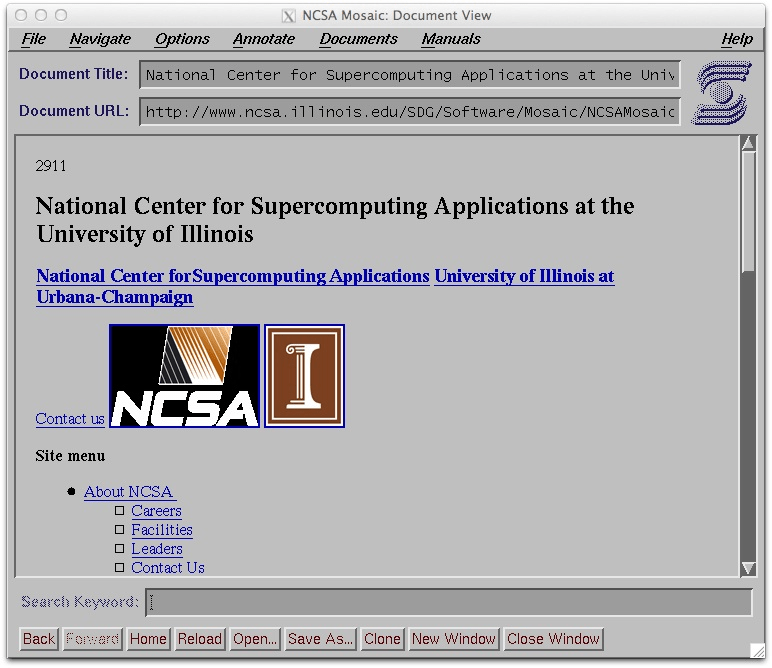
The first graphical web browser, Mosaic, was developed by Marc Andreessen and Eric Bina in 1993. Mosaic made the web more accessible to the general public, leading to an explosion of web use and the development of numerous websites.
The Dot-Com Boom and Bust
The late 1990s saw a surge in internet-based companies, leading to the dot-com boom. Companies like Amazon, eBay, and Google emerged as major players. However, the bubble burst in 2000, leading to significant losses but also setting the stage for more sustainable growth in the following years.
The Internet in the 21st Century
Broadband and Wi-Fi
The introduction of broadband internet and Wi-Fi technology in the early 2000s revolutionized internet access, allowing for faster and more reliable connections. This advancement made it easier for users to stay connected from anywhere.
The Rise of Social Media
Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram transformed the internet into a space for social interaction and networking. These platforms have become integral to communication, marketing, and information sharing.
Mobile Internet and Smartphones
The proliferation of smartphones has brought the internet into the pockets of billions of people worldwide. Mobile internet access has changed how people interact with the digital world, emphasizing the importance of mobile-friendly content and applications.
Internet Governance and Regulation
The Role of ICANN
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) was established in 1998 to coordinate the global domain name system and IP addressing. ICANN plays a critical role in maintaining the stability and security of the internet.
Net Neutrality
Net neutrality, the principle that all internet traffic should be treated equally, has been a contentious issue. Debates over net neutrality regulations have significant implications for internet access, innovation, and competition.
Privacy and Security Concerns
As the internet has grown, so have concerns about privacy and security. Issues such as data breaches, surveillance, and the spread of misinformation have prompted calls for stronger regulations and better security practices.
The Future of the Internet
The Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the growing network of connected devices that communicate with each other over the internet. IoT has the potential to revolutionize industries, from healthcare to transportation, by enabling smarter, more efficient systems.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are driving the next wave of internet innovation. These technologies are being integrated into various online services, enhancing user experiences and enabling new capabilities.
The Expansion of 5G
The rollout of 5G networks promises to deliver faster internet speeds and lower latency, enabling new applications and services. 5G is expected to support the growth of IoT, AI, and other emerging technologies.
The Global Impact of the Internet

Economic Growth and E-Commerce
The internet has significantly impacted the global economy, driving growth and creating new business opportunities. E-commerce has become a major sector, with online shopping becoming the norm for many consumers.
Education and Knowledge Sharing
The internet has democratized access to information and education. Online courses, digital libraries, and educational platforms have made learning more accessible to people around the world.
Social and Cultural Changes
The internet has changed how people interact, share, and express themselves. It has facilitated the spread of culture, ideas, and social movements, connecting people across the globe.
Frequently Asked Questions
What was the first message sent over the ARPANET?
The first message sent over the ARPANET was “LO,” which was intended to be “LOGIN.” However, the system crashed after transmitting the first two letters.
Who is considered the father of the internet?
Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn are often referred to as the fathers of the internet for their development of the TCP/IP protocols.
When was the World Wide Web introduced?
The World Wide Web was introduced in 1989 by Tim Berners-Lee, with the first website going live in 1991.
What was the first web browser?
The first web browser was WorldWideWeb, later renamed Nexus, created by Tim Berners-Lee. However, Mosaic, developed in 1993, was the first graphical web browser.
How did the dot-com bubble burst?
The dot-com bubble burst in 2000 due to a combination of overly optimistic investments in internet-based companies and the realization that many of these companies were not profitable.
What is net neutrality?
Net neutrality is the principle that all internet traffic should be treated equally, without discrimination or preferential treatment for certain services or websites.
Conclusion
The history of the internet is a story of innovation, collaboration, and transformation. From its humble beginnings as a military project to its current status as a global network connecting billions of people, the internet has reshaped society in countless ways. As technology continues to evolve, the internet will undoubtedly play a central role in shaping the future. Understanding its past helps us appreciate its impact and anticipate its potential.
Here are some external links that provide valuable information on the history of the internet:
- Internet Society: Brief History of the Internet
- History.com: The Invention of the Internet
- Computer History Museum: The Internet History
- Britannica: History of the Internet
- Web Foundation: History of the Web



